
Modern enterprises teeter on a tightrope in today’s digital landscape, constantly under siege by sophisticated cyber threats. Conventional security measures, once a sturdy bridge, now resemble a fraying net, offering little protection from a determined attacker.
The digital revolution is forcing businesses to hit the refresh button on their security strategies. Gone are the days of blind trust within network walls. Zero Trust, a groundbreaking approach to cybersecurity, emerges as the champion, challenging this outdated notion and offering a more robust defense.
The castle-and-moat security model prioritizes securing the network perimeter, similar to a fortified castle with a moat. This approach focuses on keeping external threats at bay. In the past, when most resources and users resided within a company’s network, this model offered a sufficient level of security.
However, in today’s distributed and cloud-based environment, this model leaves organizations vulnerable. With remote workers accessing corporate resources from various locations, and data flowing freely between on-premises and cloud environments, the traditional network perimeter has become increasingly porous and difficult to define.
Moreover, the castle-and-moat approach fails to address the ever-growing threat of insider attacks, where malicious actors may already have access to the network and can move laterally to compromise sensitive data and systems.
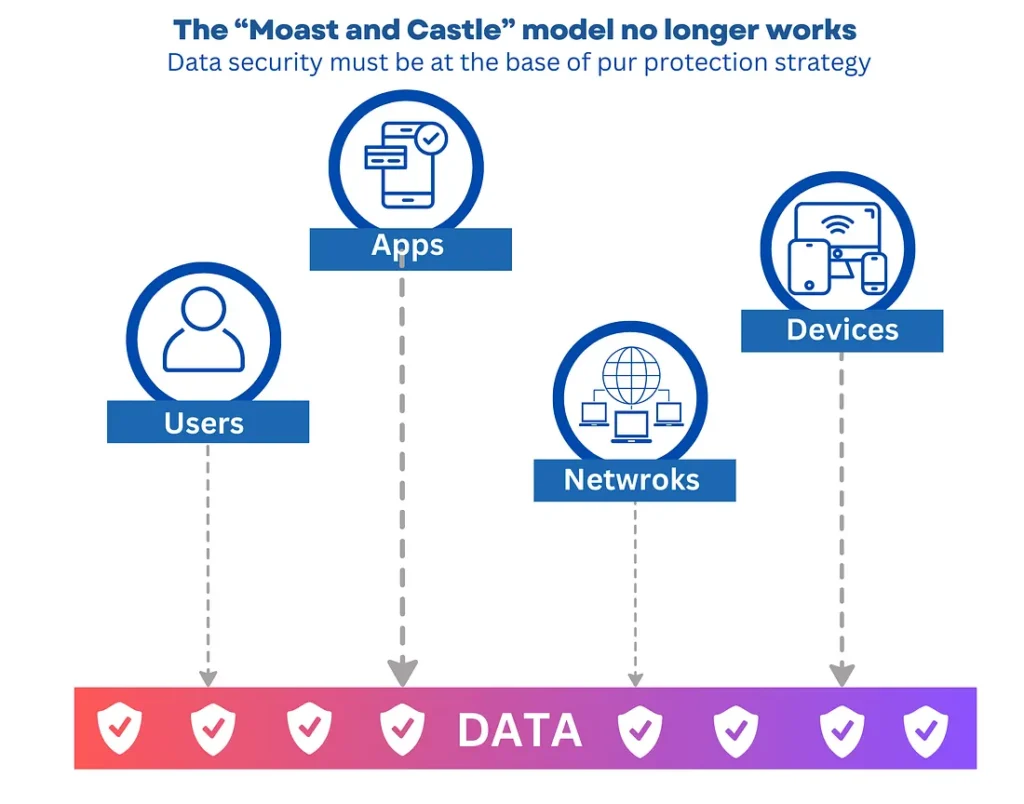
Forget the castle walls, it’s all open gates in Zero Trust security! This approach ditches the traditional “trust everyone inside” model and constantly verifies every user, device, and application trying to access resources. Like a vigilant bouncer at an exclusive club, Zero Trust says, “Prove it!” before granting access.
This “never trust, always verify” principle ensures that only authorized users get to specific resources, based on pre-set rules and real-time threat checks. The benefit? Zero Trust throws up roadblocks for both external attackers and sneaky insiders, keeping your data and systems safe even if someone breaches the network perimeter.
At the heart of the Zero Trust security model lies Identity and Access Management (IAM), a critical component that enables organizations to effectively manage and control access to their digital assets.
IAM plays a crucial role in implementing Zero Trust by:
By leveraging IAM solutions, organizations can effectively implement Zero Trust principles, ensuring that access to critical resources is granted only to authorized entities, based on real-time risk assessments and predefined policies.
The digital landscape is a battlefield in constant flux which demands a proactive, adaptable approach to counter the ever-evolving cyber threats. Shifting to Zero Trust provides a security model that prioritizes continuous verification and least privileged access. This shift empowers businesses to thrive in a dynamic environment, where trust is earned, not assumed, and every interaction is a potential security checkpoint. By embracing Zero Trust, organizations can move beyond the limitations of outdated defenses and build a resilient security posture that safeguards their digital assets in the face of tomorrow’s threats.
At ZTrust, we understand that cybersecurity is an ongoing journey, not a destination. That’s why we’ve implemented a Zero Trust security model, a powerful approach that prioritizes continuous verification and least privilege access.
This Zero Trust framework safeguards your data through a multi-layered approach, including Multi-Factor Authentication for enhanced login security, Identity and Access Management for granular control, Continuous Monitoring for real-time threat detection, Microsegmentation to limit attacker movement, and Data Loss Prevention to protect sensitive information — fostering a culture of vigilance and adapting to ever-evolving threats.
Single Sign-On (SSO) offers a range of benefits for streamlining access management and enhancing security
Keeping track of many identities and passwords for different programs may be a challenging endeavor.
In today’s complex digital landscape, organizations face the daunting task of securing their critical assets